0x01 时间函数之间的关系
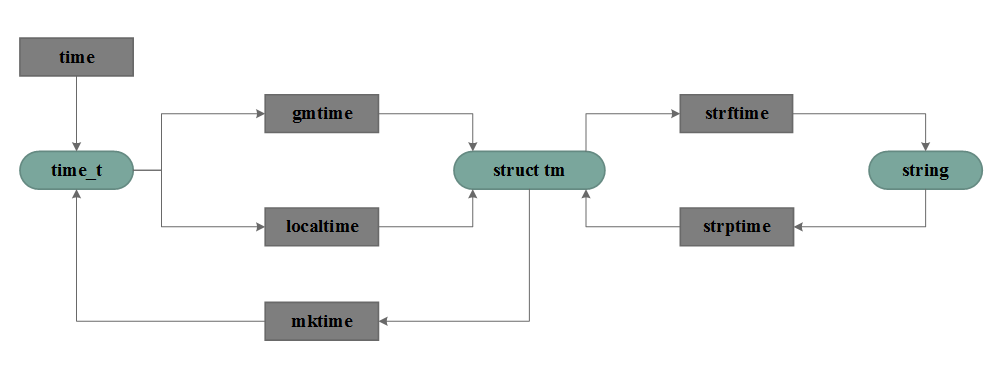
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| struct tm
{
int tm_sec; // 代表目前秒数,正常范围0-59,但允许至61秒;
int tm_min; // 代表目前分数,范围为0-59。
int tm_hour; // 从午夜算起的小时数,范围为0-23。
int tm_mday; // 目前月份的日数,范围为1-31。
int tm_mon; // 代表目前月份,从一月算起,范围为0-11。
int tm_year; // 从1900年算起至今的年数。比如(时间戳1970-01-02 10:23:09,该值为70)。
int tm_wday; // 一星期中的日数,从星期日算起,范围为0-6。
int tm_yday; // 从1月1日算起至今的天数,范围为:0-365。
int tm_isdst; // 日光节约时间的旗标。
};
|
1
2
| #include <time.h>
time_t time(time_t * t);
|
此函数会返回从公元1970年1月1日的UTC时间从0时0分0秒算起到现在所经过的秒数。如果t并非空指针的话,此函数也会将返回值存到t指针所指的内存。如果失败则返回((time_t)-1)。
1
2
| #include <time.h>
struct tm * gmtime(const time_t * timep);
|
该函数将参数timep所指的time_t结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构tm返回。该返回值代表目前的UTC时间。
1
2
| #include <time.h>
struct tm * localtime(const time_t * timep);
|
该函数将参数timep所指的time_t结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构tm返回。该返回值代表目前的当地时区的当地时间。
1
2
| #include <time.h>
time_t mktime(struct tm * timeptr);
|
该函数将参数timeptr所指的tm结构数据转换成从公元1970年1月1日0时0分0秒算起的至今的UTC时间所经过的秒数。
1
2
| #include <time.h>
size_t strftime(char *s, size_t max, const char *format, const struct tm *tm);
|
该函数将参数tm,依照参数format所指定的字符串格式做转换,转换后的字符串复制到参数s所指的字符串数组中,该字符串的最大长度为参数max所控制。
1
2
| #include <time.h>
char *strptime(const char *s, const char *format, struct tm *tm);
|
该函数将参数s所指定的按一定格式要求编制的字符串,根据格式化参数format,转换成tm结构的值。如果分析错误,返回NULL。
0x02 strftime和strptime的格式参数
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|
| %a | 星期几的简写 |
| %A | 星期几的全称 |
| %A | 星期几的全称 |
| %b | 月分的简写 |
| %B | 月份的全称 |
| %c | 标准的日期的时间串 |
| %C | 年份的前两位数字,比如1997年表示为:19 |
| %d | 十进制表示的每月的第几天,表示法为:01-31 |
| %D | 格式为“月/天/年”表示时间。相当于“%m%d%y”格式。例如“19970701” |
| %e | 十进制表示的每月的第几天(不补0),表示法为:1-31。 |
| %F | 使用“%Y-%m-%d”格式表示日期。例如“1997-07-01”。 |
| %g | 年份的后两位数字,比如1997年表示为:97 |
| %G | 完整的公元年份表示,比如1997年表示:1997 |
| %h | 同“%b”一样,简写的月份名。 |
| %H | 以24小时制表示小时数(00-23)。 |
| %I | 以12小时制表示小时数(01-12)。 |
| %j | 十进制表示一年中的天数(001-366)。 |
| %k | 同“%H”,表示法为:0-23 |
| %l | 同“%I”,表示法为:1-12。 |
| %m | 十进制表示的月份,表示法:01-12。 |
| %M | 十时制表示的分钟数,表示法:00-59。 |
| %n | 同“\n”,换行。 |
| %p | 本地AM或PM的等价显示。 |
| %P | 同“%p”相似,但使用小写的am和pm来表示。 |
| %r | 相当于使用“%I:%M:%S %p”格式,例如:“08:31:50 PM”。 |
| %R | 相当于使用“%H:%M”格式,例如:“22:31”。 |
| %S | 十进制的秒数,表示法:00-59。 |
| %t | 水平制表符,同“\t” |
| %T | 24小时时间表示,相当于“%H:%M:%S”格式。 |
| %u | 一星期中的星期日期,范围:1-7,星期一从1开始。 |
| %U | 一年中的星期数,范围:00-53,一月第一个星期日开始为01。 |
| %V | 一年中的星期数,范围:00-53,一月第一个星期一开始为01。 |
| %w | 一星期中的星期日期,范围:0-6,星期日从0开始。 |
| %W | 一年中的星期数,范围:00-53,一月第一个星期一开始为01。 |
| %x | 标准的日期串。比如2017年1月2日,表示成:“01/02/17”。 |
| %X | 标准的时间串。比如2017年1月2日10点23分9秒,表示成:“10:23:09”。 |
| %y | 不带世纪的十进制年份(值从0到99) |
| %Y | 带世纪部分的十制年份 |
| %z,%Z | 时区名称,如果不能得到时区名称则返回空字符。 |
| %% | 百分号 |
关于%U参数:
比如2017年的1月1日是星期日,使用%U得到的值是“01”
比如2016年的1月1日是星期五,使用%U得到的值是“00”
关于%V参数:
比如2017年的1月1日是星期日,使用%V得到的值是“52”
比如2017年的1月1日是星期一,使用%V得到的值是“01”
比如2016年的1月1日是星期五,使用%V得到的值是“53”
0x03 使用示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| #include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
std::string Timestamp2Str(const time_t iTimestamp, const std::string& sFormat)
{
struct tm xTime = { 0 };
::localtime_r((time_t*)&iTimestamp, &xTime);
char szTimeString[255] = "\0";
::strftime(szTimeString, sizeof(szTimeString), sFormat.c_str(), &xTime);
return std::string(szTimeString);
}
int32_t Str2Timestamp(const std::string& sTimeStr, const std::string& sFormat)
{
struct tm xTime = { 0 };
if (::strptime(sTimeStr.c_str(), sFormat.c_str(), &xTime) == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
return ::mktime(&xTime);
}
std::string GetCurrentDateTime(const std::string &sFormat = "%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
{
return Timestamp2Str(::time(NULL), sFormat);
}
int32_t GetCurrentTimestamp()
{
return time(NULL);
}
uint64_t GetCurrentTimestampMS()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return tv.tv_sec*1000LL + tv.tv_usec/1000;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "GetCurrentTimestamp : " << GetCurrentTimestamp() << std::endl;
std::cout << "GetCurrentTimestampMS : " << GetCurrentTimestampMS() << std::endl;
std::cout << "GetCurrentDateTime : " << GetCurrentDateTime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S") << std::endl;
std::cout << "GetCurrentDateTime : " << GetCurrentDateTime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") << std::endl;
return 0;
}
|
